Custos Aeris: New evaluations for the preventive protection of historical lead glazing (Part 3)

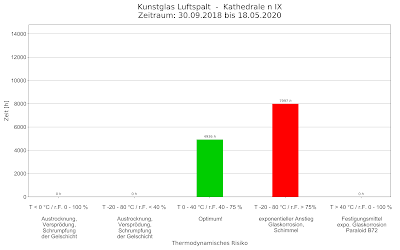
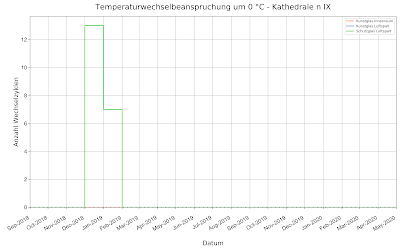
Risk Temperature and humidity alternating stress Risk of thermal cycling Thermal cycling around 0 degrees Celsius leads to the formation of ice and condensation. Solid and liquid phases change constantly. This leads to mechanical damage to the gel layer and cracks, crusts, cracking and detachment /Hör 06/. There are still no limits as to how often this may happen per defined time unit except "as little as possible". The following diagram shows the number of changes per time unit for protective glazing in a cathedral: Number of Thermal Cycles around 0 degrees C Risk of moisture cycling Moisture cycling around 80% leads to salt crystallization, cracking of the gel layer and intensification of corrosion /Hör 06/. Here too, there are no limit values, so that again the number of changes per unit of time is shown: Number of moisture Cycles around 80% relative humidity References: Garrecht, H., Hahn, O. & Kappes, K. e., 2010. model test for gap temperature control at the Divi Bl...